ffmpeg basic concept
ffmpeg java demo
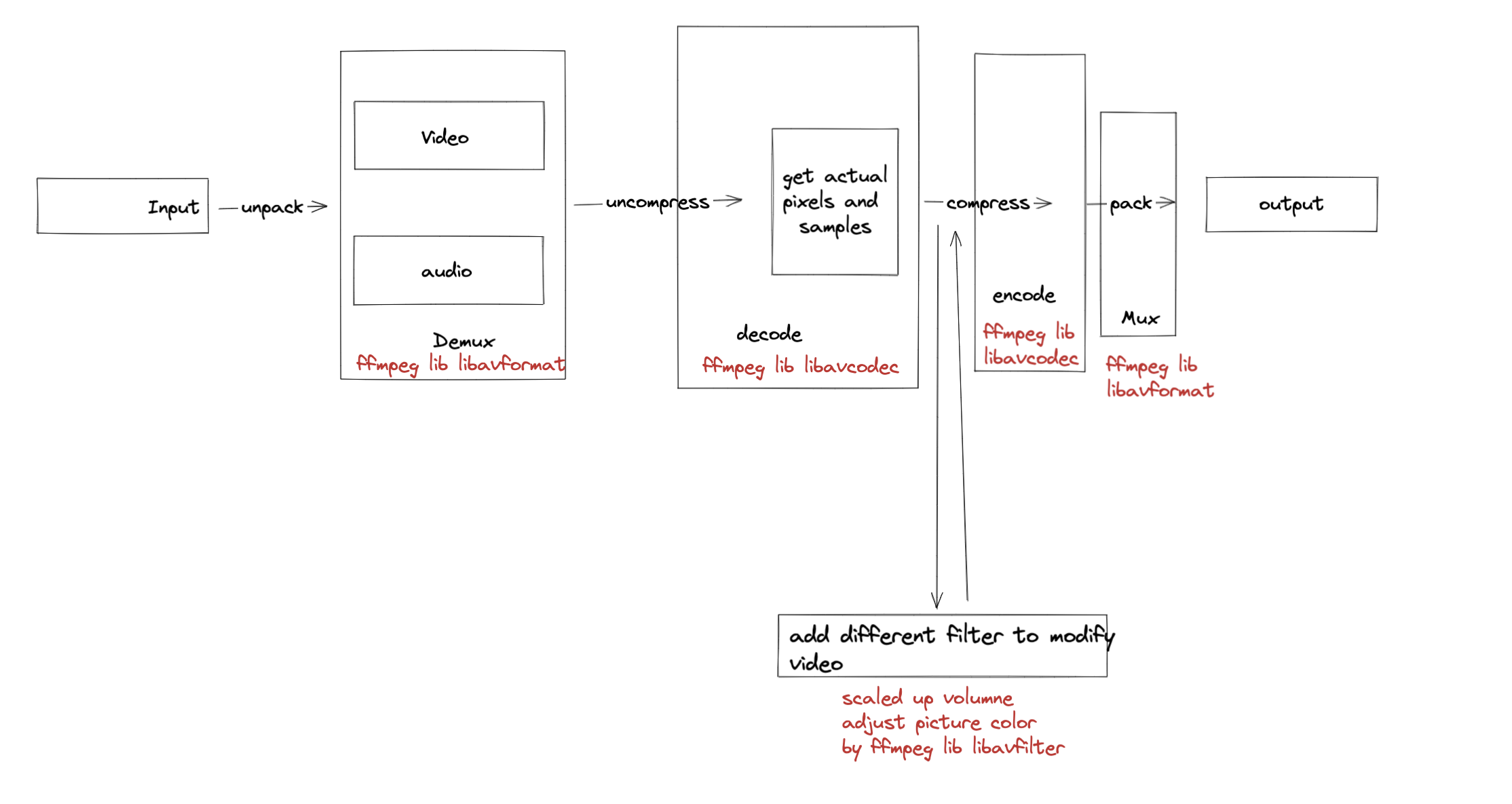
- What is ffmpeg
- High frequency using library
- libavcodec, contains all encoders and decoders, which is used to encode or decode the resource you input
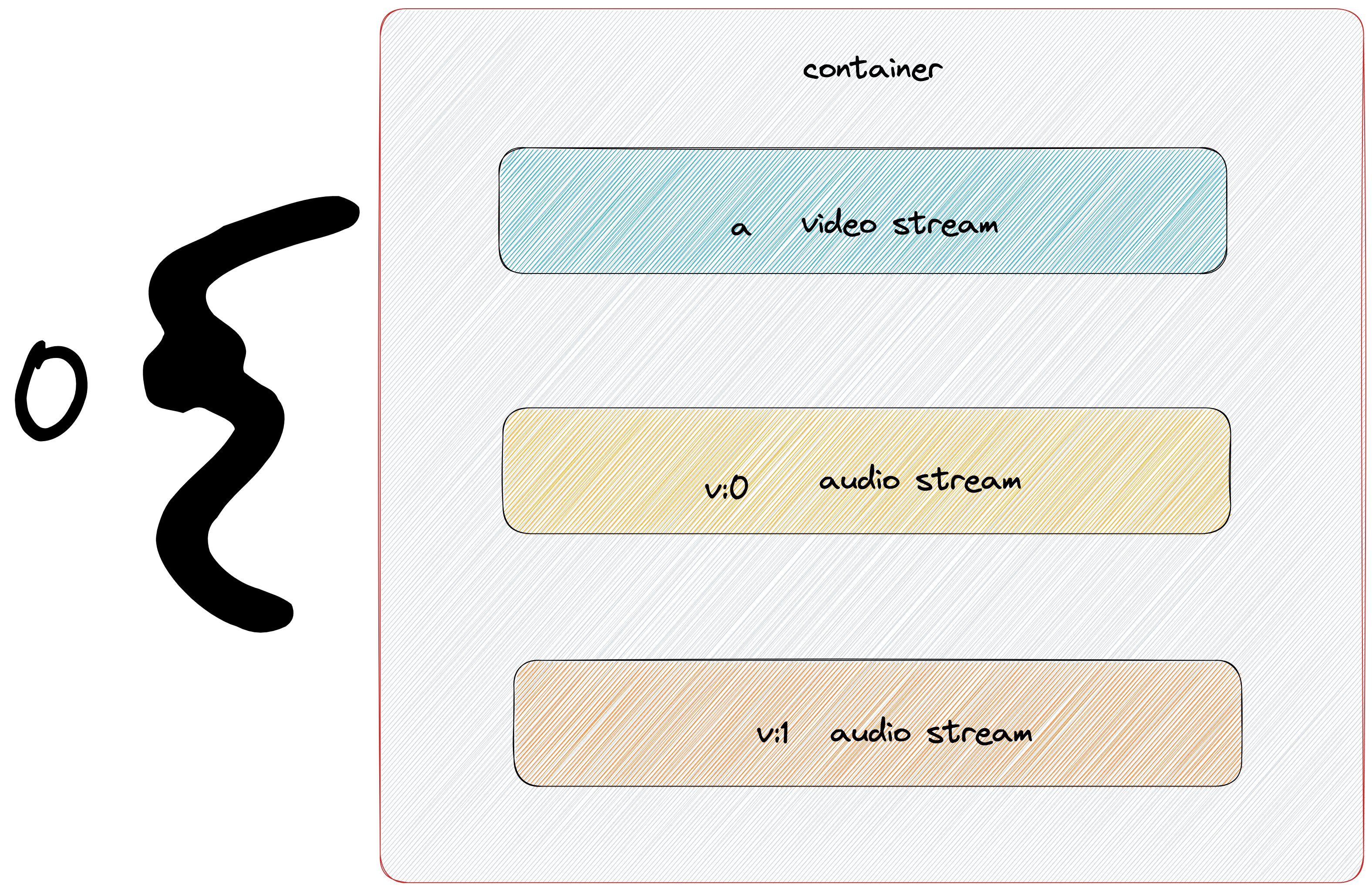
- libavformat, deal with the muxers or demuxers for various container. container is a file which is used to save your video, audio streams, and anyclose what is muxer and demuxer in pic?
- libavfilter, used to modify audio or video
- libavdevice, used to support different input and output devices
- libavutil,
- libwscale,
- libswreasample
- ffmpeg package tools
- ffmpeg, itself is a command line tool which is used to process the video or audio resource
- ffplay, which is a minimal video player, you can use it play a large wide of video format
- ffprobe, which is used to extract video or audio information
Media Concepts
- image
- pixel, is a 2D point, has color RGB or YUV, alpha value transparency
- resolution, the quality of the image of the number of pixel of the image
- Aspect Ratio, the radio of the width and height
- Audio
- smallest digital representation of a sound
- 8/16/24/32 bit value, more bits means high quality video source
- audio frequency, how many samples during the per second, the higher, the higher quality
- audio channel, which means that several audios will be played together
- for example, one audio channel is named ‘Mono’, two is named ‘Stereo’ and both of them are called
channel layouts
- for example, one audio channel is named ‘Mono’, two is named ‘Stereo’ and both of them are called
- audio track, organize different audio channels
- for example, an audio can obtain multilingual channel, an English channel or a French chanel, and also it can take a background chanel, some of them can be mixed
- Video
- sequence of images, has the time duration, Each image is called a frame
- Video frame rate(FPS), Frame per second
- video compression, not very clear about the concept? remove redundant information, Spatial redundancy (within frame), Temporal redundancy (across frame). How to make it?
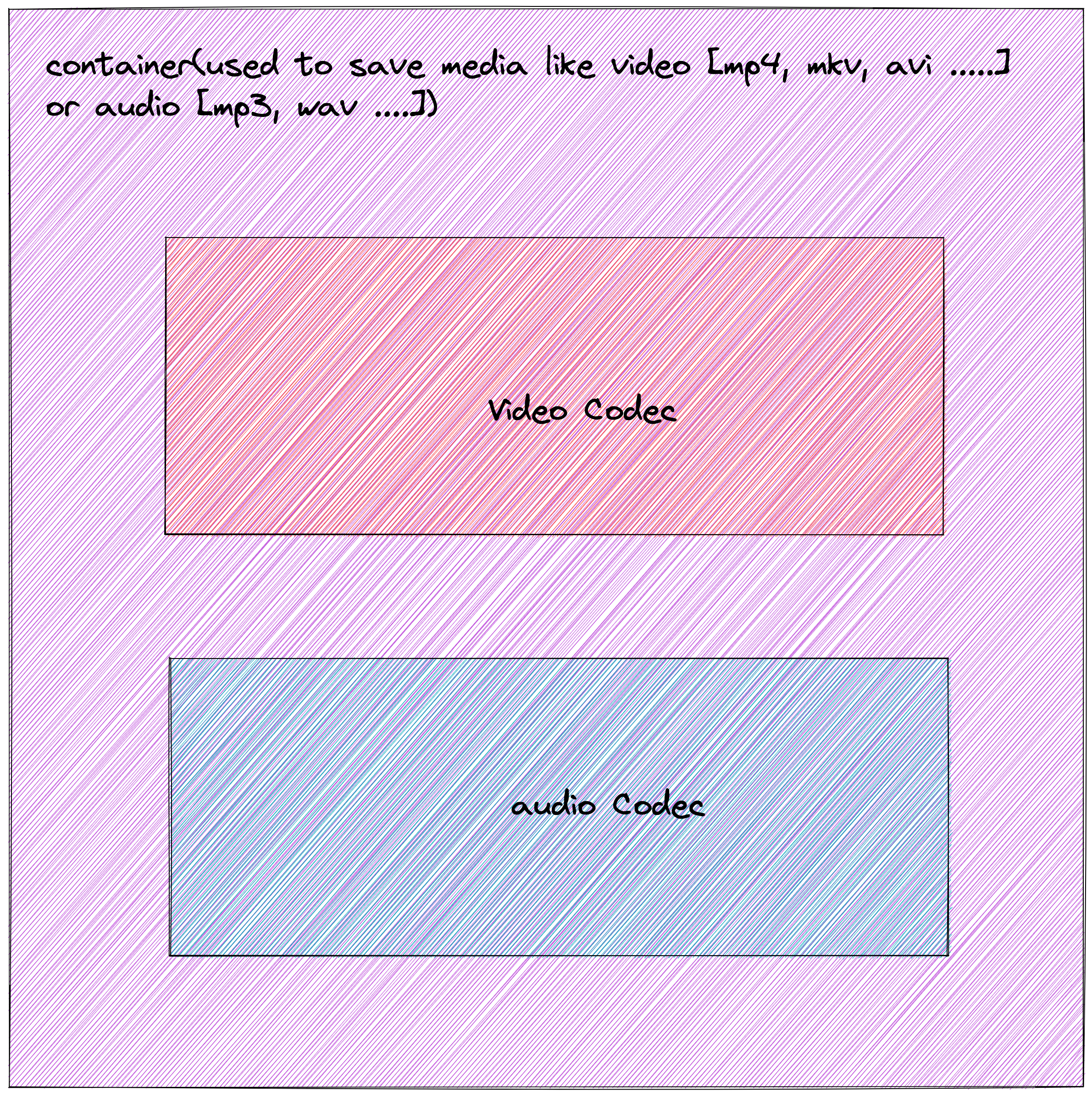
- Codec & Container

- Codec
- encode, because video is a very big file, if we transfer it directly, which is an impractical idea. and decode is used to play the video
- some encode algorithm
- video, H.264, H.265, VP9, Prores, DNxHd,
- audio, PCM, AAC, MP3
- the benefits of different codec algorithm
- Container
- use to package or wrapper a media file
- format
- video, MP4, MXF, QT/MOV, MKV
- audio, WAV, M4A
- Codec
- Transcoding
- transfer one codec to another one
- why we need transcode, because it depends on different situation, sometimes, we need take care of quality, being smaller during the transporting in the internet
- using scenario
- Transmuxing, From one container to another
- thumbnail generation, preview image, search hit, hover-scrubbing on the web page, poster frame
- Frame rate conversion
- support different TV standards
- higher FPS: preserve slow motion quality for editing
- lower FPS: playback or streaming
- Bitrate conversion
- quality the higher bitrate the higher quality
- smaller storage space
- support different network bandwidth
- change GOP size
- good for editing based on I-frame (keyframe) only, 保持一个关键帧,然后可以继续操作,就可以得到动画
- good for compression and streaming based on long GOP
- overlay
- logo ….
- subtitle/capture
- timecode
- covert video resolution
- Audio volume adjustment
- Audio mixing eg: mix the person speaking voice and the background voice
- audio resampling, changing the frequency
How to setup it?
- how to get it?
- No official builds
- Build from source code, download it from
githubrepo - Download Pre-build packages, Use package management tool, like
homebrewandAPT
- support OS
- macOS
brew install ffmpeg - linux
- Windows
- macOS
How to use its sub-component tool
- ffprobe
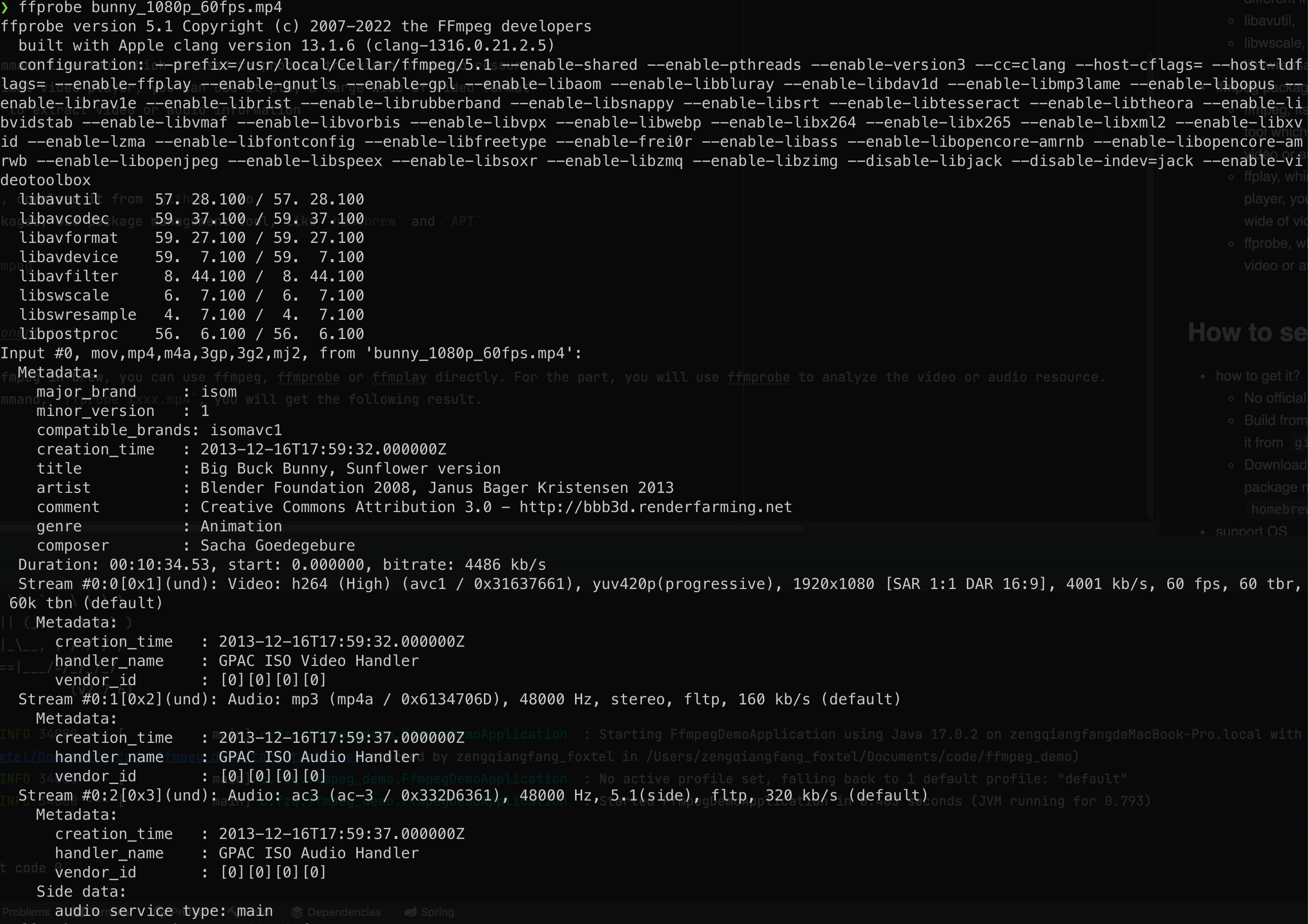
- When you install the ffmpeg in brew, you can use ffmpeg, ffmprobe or ffmplay directly. For the part, you will use ffmprobe to analyze the video or audio resource.
- Input the following command,
ffprobe xxxx.mp4, you will get the following result with log. * If you don't need any log, you can input the following command, `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format`, you will retrieve the whole video format details
* If you want to know the details of the stream, you can input `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format -show_streams` * with parameter `-print_format`, you can only **format** output csv or json
* If you don't need any log, you can input the following command, `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format`, you will retrieve the whole video format details
* If you want to know the details of the stream, you can input `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format -show_streams` * with parameter `-print_format`, you can only **format** output csv or json1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21[FORMAT]
filename=bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4
nb_streams=3
nb_programs=0
format_name=mov,mp4,m4a,3gp,3g2,mj2
format_long_name=QuickTime / MOV
start_time=0.000000
duration=634.533333
size=355856562
bit_rate=4486529
probe_score=100
TAG:major_brand=isom
TAG:minor_version=1
TAG:compatible_brands=isomavc1
TAG:creation_time=2013-12-16T17:59:32.000000Z
TAG:title=Big Buck Bunny, Sunflower version
TAG:artist=Blender Foundation 2008, Janus Bager Kristensen 2013
TAG:comment=Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 - http://bbb3d.renderfarming.net
TAG:genre=Animation
TAG:composer=Sacha Goedegebure
[/FORMAT]* with parameter `-show_stream -select-streams v`, only output video stream1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15{
"programs": [],
"streams": [
{
"codec_name": "h264"
},
{
"codec_name": "mp3"
},
{
"codec_name": "ac3",
"side_data_list": [{}]
}
]
}* with parameter `-show_entries stream=codec_name`, only output codec name, you might need to remove the other parameters like `-show_stream` or `-show_format` * with parameter `-print_format default=noprint_wrappers=1`, remove outside tag1
2
3
4
5{
"programs": [],
"streams": [{
"codec_name": "h264"}]
}* with parameter `-print_format default=noprint_wrappers=1:nokey=1`, you can get the only value without key1
2
3codec_name=h264
codec_name=mp3
codec_name=ac3* You can analyze the stream information by URL directly without downloading it to loacl machine `ffprobe -v error1
2
3h264
mp3
ac3` * [more details, www.ffmpeg.org/ffprobe.html](https://www.ffmpeg.org/ffprobe.html)
- ffplay
- with the parameter
-x , -y, you can control the size of the video window - with the parameter
-noborder, you can remove the border of the video window - with the parameter
-top -left, you can control the position of the video window - with the parameter
-fs, you can get the full screen video window - with the parameter
-an, you can disable the audio - with the parameter
vn, you can disable the video- tips, you can press key
Wto switch the show-mode
- tips, you can press key
- with the parameter
-showmode waves, you can get the video wave - with the parameter
-loop <times>, you can get looping video - with pressing key
S, you can step through the frames of a video one frame at a time
- with the parameter
- ffmpeg
- overview of how to edit media

- details
- input & output
ffmpeg -i <protocol>:<device>, file is default, you also can choose the network pattern, like http, ftp, rtp etc.- according to the above processing, you can run the following command like
ffmpeg -i input.mov ...add some filter... output.mp4 - with the parameter,
-f extension, you can do the muxing or demux use the command. During the input process, it was used to demux. During the output process, it was used to mux.ffmpeg -i input.mov ... -f ... output.extension
- with parameter
pipe:0, don’t know very well - capture, I guess this can be used to record screen;
ffmpeg -f avfoundation -list_devices true -i ""list the useful device in the current machine- screen
ffmpeg -f avfoundation -i ":1" ....
- audio (microphone)
ffmpeg -f avfoundation -i ":2" ....
- webcam
ffmpeg -f avfoundation -i "default" ....
- testing
ffmpeg -f lavfi -i color=color=red..., lavfi is a virtual space
- stream selection

- For one container, generally speaking, it includes one video stream and one more audios streams
- how to select a stream,
: : , these three inputs will control the stream you want to select. ffmpeg -v error -y -i bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -to 1 bunny_1080p_60fps-1s.mp4, the command is used to edit a video-yoverride the file anyway-tocut the video until 1 second- For default, ffmpeg only picks up one video and one audio
- get all, with parameter
-map 0 - get video, with parameter
-map 0:v - get audio, with parameter
-map 0:a - get first audio, with parameter
-map 0:a:0
- get all, with parameter
- You also can process multiple data together, integration some video, layout(logo), audio together
ffmpeg -v error -y -i bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -i bullfinch.mov -to 1 -map 0:v:0 -map 1:a:0 bunny_1080p_60fps-1s-mix.mp4
- filter
- do some change for the media, the common library is
libavfilter - syntax, filter=key1=values:key2=value2
- eg: scale filter scale=width=1920:height=1080
- different filter labels are used
; [semicolon sign]to split each others. In my opinion, I think that semicolon sign is used to do the textual separation, which the filter is more readable. - for one filter with multiple options, using
: [colon sign]to split each other - using comma
,to split the different filter
- different filter labels are used
- eg: scale filter scale=width=1920:height=1080
- it can be labeled, which can be referred for later option
- filter graph
- with param
-vfprocess graphs with single input and output, especially operate video resource - eg:
1
2
3
4
5ffmpeg -v error -i <medida name with extension> -vf
"split[bg][ol]; // split the media with the same two parts
[bg]scale=width=1920:height=1080,format=gray[bg_output];
[ol]scale=-1:480,hflip[ol_output];
[bg_output][ol_output]overlay=x=W-w:y=(H-h)/2" <ouput file > // combine two outputs togther. - with param
-filter-complex, you can manipulate all the streams, like video, audio and picture.1
2
3
4
5ffmpeg -v error -y -i bullfinch.mov -i logo.png -filter_complex
"[1:v]scale=-1:200[s_logo];
[0:v][s_logo]overlay=x=W-w-50:y=H-h-50,split=2[sd_in][hd_in];
[sd_in]scale=-2:480[sd];[hd_in]scale=-2:1080[hd]"
-map \[sd\] bully-sd.mp4 -map \[hd\] bully-hd.mp4- tips: If you want to use it in zsh, you should add escape symbol before the special character, like
'[', ']'
- tips: If you want to use it in zsh, you should add escape symbol before the special character, like
- with param
-af, you can do some editions on audio stream only for one input and output - common filter
- scale, one input and one output
- split, one input and multiple output
- overlay, multiple input and one output
- with param
- do some change for the media, the common library is
- encoding
- what is kind of thing should we take into consideration?
- compression
- quality vs size
- stream vs post-production
- target application
- compatibility, check the codec is supported by the container
- converting
- If you want to transfer one container to another and don’t set the specific codec method, ffmpeg will set a default codec (suitable one).
- eg:
ffmpeg -v error -y -i bullfinch.mov transcoded.mxf - with parameter,
-vcodec <codec name>to set specific video codec methodffmpeg -encoders, list all the useful codec method
- with parameter
-avodec, set the specific audio codec method
- eg:
- detail of AVC short for advanced video codec, H.264
- codec library: libx264
- profile, baseline, main, high, it is optional
- Rate control (edit the bitrate, effect the video quality)
- with parameter
-crf - CRF: constant quality, variable bitrate, focus on high quality crf 0-51, the higher, the worse quality
- Two-pass ABR, this is a quantitative option, with parameter
-b:v 2M, which means that the bitrate is set as 2Mbps- tips, it cannot give you very accurate bitrate, therefore you can use two pass method. like
-b:v 2M -pass 1 -f null /dev/null, then-b:v 2M -pass 2 filename. The result of the first step will be saved into the statics
- tips, it cannot give you very accurate bitrate, therefore you can use two pass method. like
- preset, which is used to control the speed of compression, the quicker, the bigger compression file you get
- with parameter
- If you want to transfer one container to another and don’t set the specific codec method, ffmpeg will set a default codec (suitable one).
- what is kind of thing should we take into consideration?
- Streaming
- Basic Concept
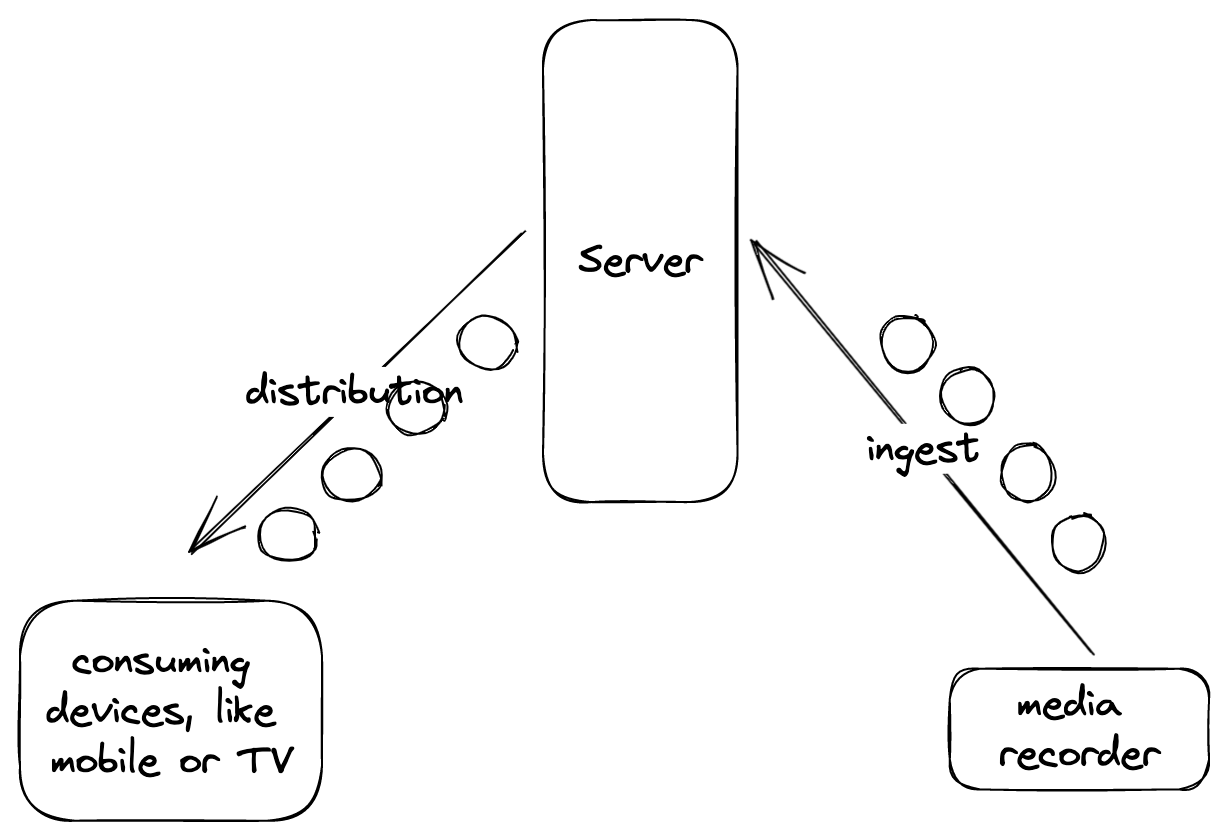
- The device connect to the internet, then you can get the media resource from the internet transportation, rather than download the media directly. This process can be called as streaming.
- And the streaming can be consumed without any waiting just watch it directly when your device connects to the internet

- Streaming playback, it is a mechanism for keep a comfortable watching experience.
- Playable instantly, without downloading the whole media files
- Seekable, when you choose the different timeline, the media can be played based on the correct timeline rather than play it from the start
- Adaptive, based on different network situation (adaptive streaming bitrate, how to make it? not only the network situation, but also the player window size)
- In my opinion, it will start with a file extended with
m3u8. Actually, the following playable videos are separated very small parts whose format ists. When the network becomes worse, it will retrieve some low bitrate media resource until the network turn to the good situation.
- In my opinion, it will start with a file extended with
- Streaming protocol
- different protocol is suitable to different situations, some are applicable to ingest, some are for distribution.
- RTMP
- real-time-messaging protocol
- based on TCP
- low latency
- stop updating, so not support to latest codec method
- required flash plugin
- is popular to live-streaming ingest
- HTTP
- widest reach
- TCP based
- unlikely to be blocked anywhere
- support its native player
HTML5 video, no need to add extra plugin, like flash - native support HLS and MPEG-DASH adaptive method
- good at distribution, not widely used to ingest
- SRT
- secure reliable transport
- based on UDP based
- faster than RTMP
- cannot support any browsers, because its based on UDP, but it’s extremely applicable to ingest streaming
- RTMP
- different protocol is suitable to different situations, some are applicable to ingest, some are for distribution.
- Progressive Download
- The progressive download method downloads and caches video on the viewer’s device. A short period of time is required to buffer and cache the beginning of the media file before it starts playing
- single-file media
- advantage
- Not segmented
- Easier to handle
- native browser support
- copy and download easily, you can send the whole file to other services
- advantage
- container formats
- MP4, WebM, Ogg, these formats are supported by native browser
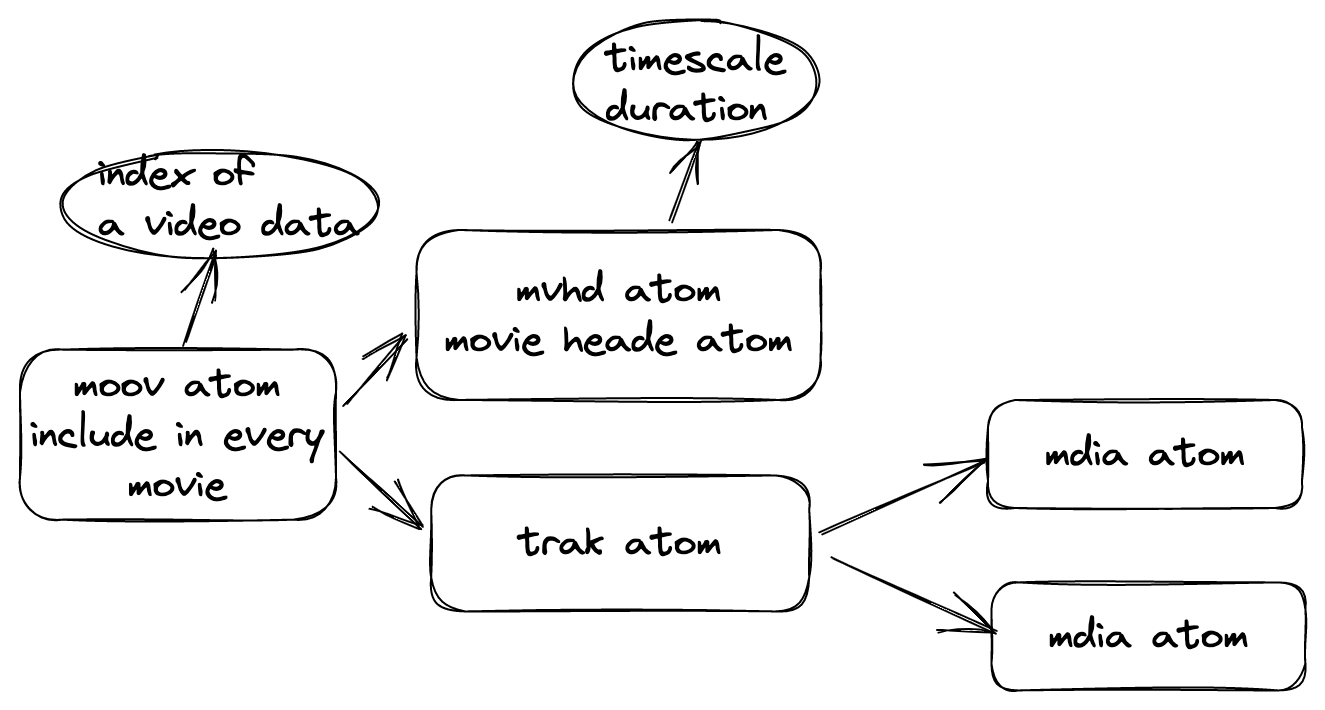
- The index
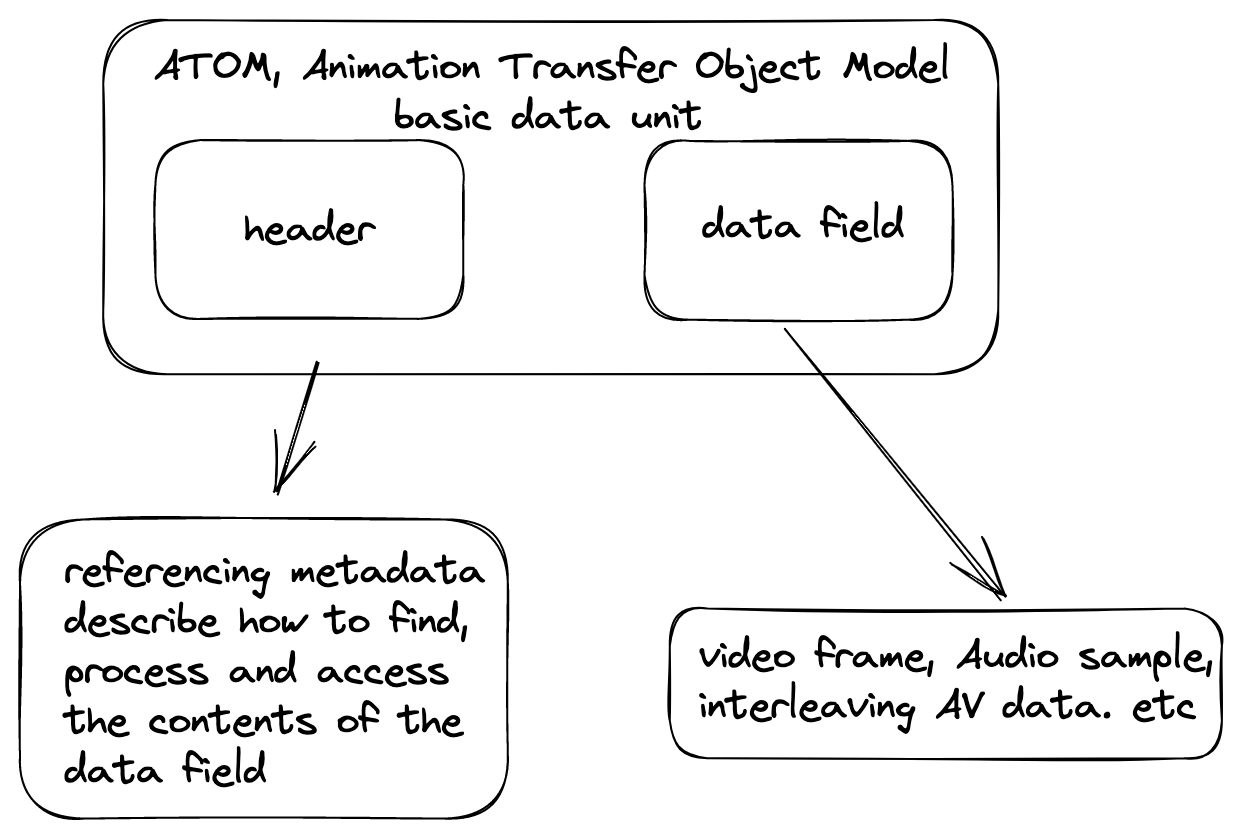
- It’s used to look up the media data of a time aor frame, just like a table or a map to save the media information
- It will be written into the end of the mp4 file
- Similar to Apple player format (QuickTime, MOV)
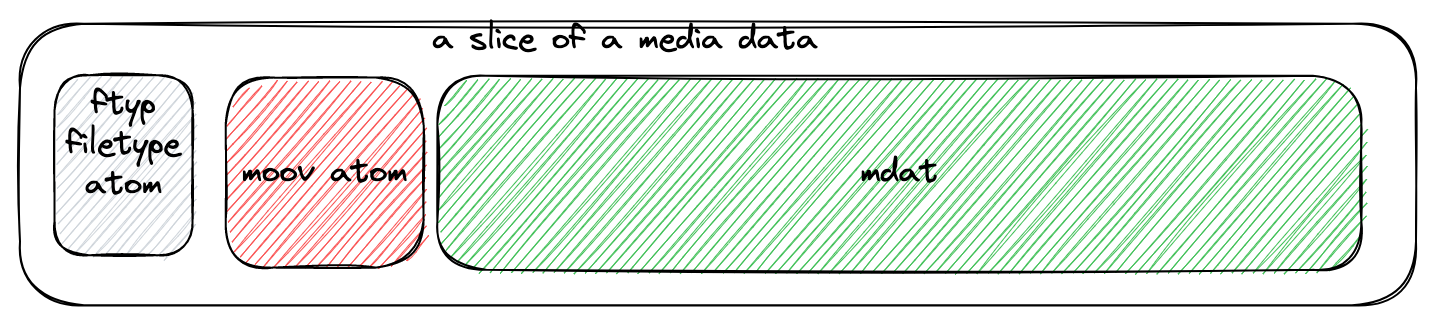
- the data will get some hierarchical sections, the section are atom/box, atom will be set into the stream during the codec period


- fast-started

- This will let the video be played gradually rather than download the whole file once time
- with command
ffmpeg -v trace -i <video name>, you can get the verbose information - pick atom
ffmpeg -v trace -i fast-start.mp4 2>&1 | grep -e type:\'mdat\' -e type:\'moov\' - convert to a fast-started media
ffmpeg -i fast-start.mp4 -movflags +faststart -c copy test-fast-started.mp4- option
-movflag
- option
- Adaptive Streaming
- Sometime, the outside condition is changeable, for single-quality media, it just only has one quality, single resolution, bitrate choice
- adaptive resolution, different screen size the stream will choose some related stream. But if the screen resolution is greater than the low standard resolution and less than the high standard resolution, it will still use the higher one, take the 560p as an example, the play will still play the 720p media.
- ffmpeg can do it?
- how it work
- adaptive streaming solution
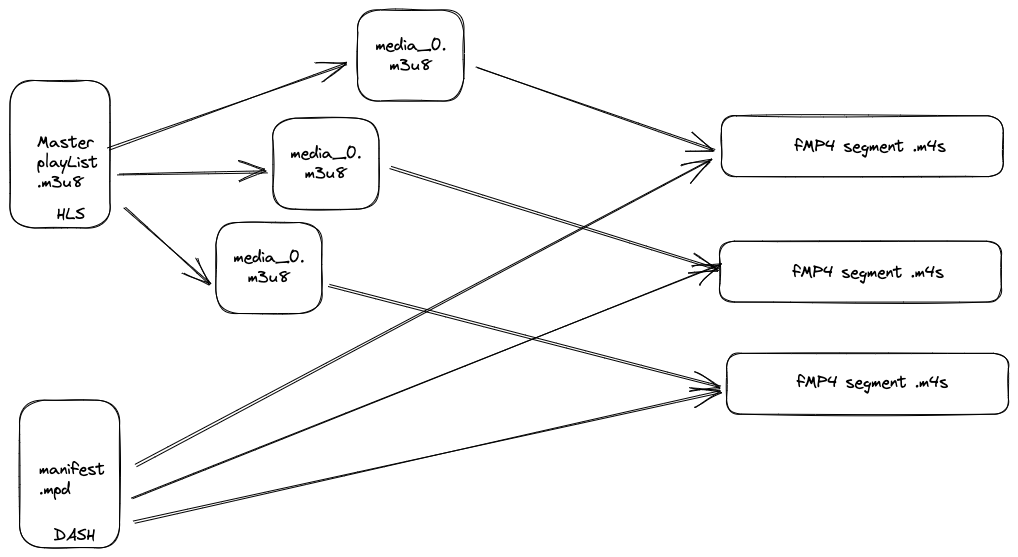
- HLS, http live streaming
- codec (H.264 avc H.265 havc)
- container (TS, fMP4, Fragmented MP4)
- manifest
- m3u8
- master playlist is used to point the media playlist
- media playlist list the individual the segments of ts file in sequence
- m3u8
- DASH, dynamic adaptive streaming over http
- MPEG-DASH (mp4)
- codec freedom, H.264, H.265, VP9, etc.
- container only fMP4
- manifest (mdp, media presentation description, format is
xml)
- common characteristics
- both can split media into several small segments
- HLS, http live streaming
- adaptive streaming solution
- the facts need to consider when encoding the media to adaptive streaming
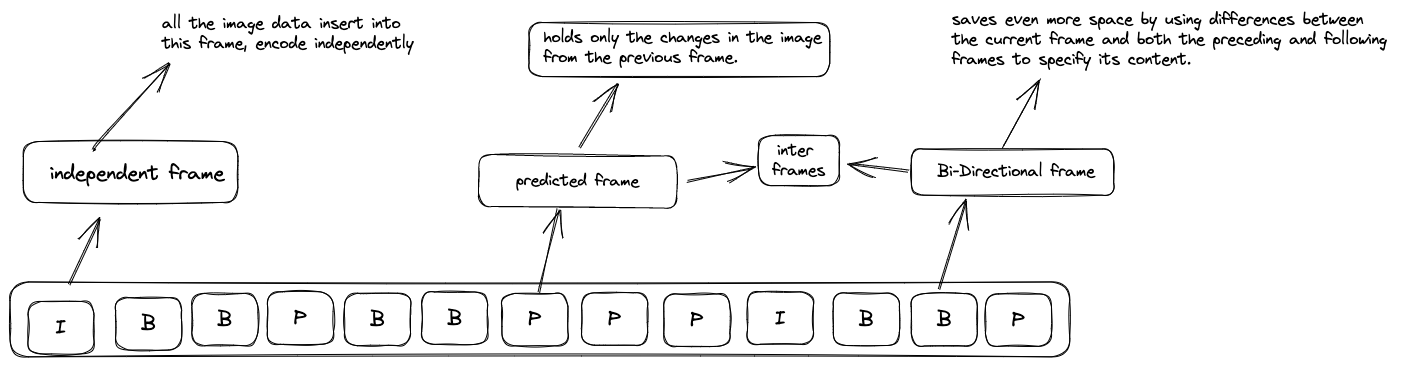
- frame type

- What is the self-contained in GOPs
- how to use ffmpeg to convert the media into HLS or DASH
- HLS, TS, A+V, the format of playlist is
m3u8and the segment istsffmpeg -y -i bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -to 10 \ -filter_complex "[0:v]fps=30,split=3[720_in][480_in][240_in];[720_in]scale=-2:720[720_out];[480_in]scale=-2:480[480_out];[240_in]scale=-2:240[240_out]" \ -map \[720_out\] -map \[480_out\] -map \[240_out\] -map 0:a -map 0:a -map 0:a \ -b:v:0 3500k -maxrate:v:0 3500k -bufsize:v:0 3500k \ -b:v:1 1690k -maxrate:v:1 1690k -bufsize:v:1 1690k \ -b:v:2 326k -maxrate:v:2 326k -bufsize:v:2 326k \ -b:a:0 128k \ -b:a:1 96k \ -b:a:2 64k \ -x264-params "keyint=60:min-keyint=60:scenecut=0" \ -var_stream_map "v:0,a:0,name:720-4M v:1,a:1,name:480-2M v:2,a:2,name:240p-500k" \ -hls_time 2 \ -hls_list_size 0 \ -hls_segment_filename adaptive-%v-%03d.ts \ -master_pl_name adaptive.m3u8 \ adaptive-%v.m3u81
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39* `-b:v:0` is used to select the video stream and set the average bitrate, like `-b:v:0 128k`;
* `-bufsize` is used to check the average bitrate in this set value. eg: `-bufsize 128k`, During each 128k media transmission, ffmpeg will calculate the current average bitrate
* if the smaller value is set, the frequency of checking bitrate will be too high. Otherwise, it will take a long duration
* Generally speaking, it can set the same as the video average bitrate or even the half of it
* `-maxrate` is used to limit the max transmission bitrate. eg: Your max bandwidth is **1024kb/s**, and assuming you can totally use this bandwidth, audio will use 128k/s (this audio is stereo, 64k per channel), therefore, only 896k/s you can use, so you should set this value as your **maxrate**
* references
* [What does -bufsize do?](https://trac.ffmpeg.org/wiki/Limiting%20the%20output%20bitrate)
* [Encoding for streaming sites](https://trac.ffmpeg.org/wiki/EncodingForStreamingSites)
* HLS, TS separate the audio and video, only single audio stream, will have itself playlist manifest
* HLS, fMP4
* DASH, fMP4
* HLS+DASH, fMP4
* 
* ```yaml
ffmpeg -y -i bullfinch.mov -to 10 \
-filter_complex "[0:v]fps=30,split=3[720_in][480_in][240_in];[720_in]scale=-2:720[720_out];[480_in]scale=-2:480[480_out];[240_in]scale=-2:240[240_out]" \
-map \[720_out\] -map \[480_out\] -map \[240_out\] -map 0:a \
-b:v:0 3500k -maxrate:v:0 3500k -bufsize:v:0 3500k \
-b:v:1 1690k -maxrate:v:1 1690k -bufsize:v:1 1690k \
-b:v:2 326k -maxrate:v:2 326k -bufsize:v:2 326k \
-b:a:2 128k \
-x264-params "keyint=60:min-keyint=60:scenecut=0" \
-hls_playlist 1 \
-hls_master_name adaptive.m3u8 \
-seg_duration 2 \
adaptive.mpd
```
* example of manipulate video
* Trimming
* `ffmpeg -y -v error -i nature.mp4 -ss 00:03:55 -to 240 bear.mp4`
* `-v [flags+]loglevel` set the processing log error verbose
* `-ss` set up the start second
* `-to` set up the total duration
* `-t` set up the segment duration, take the above command as an example, if you want to achieve the same behavior, you can use `-ss 00:03:55 -t 5`
* Merge
* define a list file
* ```text
file 'bear.mp4'
file 'flower.mp4'
- HLS, TS, A+V, the format of playlist is
ffmpeg -y -v error -f concat -i list.txt merge.mp4
- Basic Concept
- Thumbnail
ffmpeg -v error -i bullfinch.mov -vframes 1 bullfinch-poster-image.jpg-vframesset up the number of frames- You also can use filter during this processing, by the following command
ffmpeg -v error -i bullfinch.mov -vframes 1 -vf scale=320:180 bullfinch-poster-image-thumbnail.jpg
- if you don’t want to output the first frame as the thumbnail, you can add the
-ssbefore the-vframes - If you want to output multiple frame pictures, you can run the following command
ffmpeg -v error -i bullfinch.mov -vf fps=1,scale=320:180 bullfinch-thumbnail-%02d.jpg-%02dis a template syntax, which can be used to generate multiple file
- Scaling
- resize the media or photo resource
-vf scale=-2:480, minus two means we want to keep the aspect ratio- force original aspect ratio option,
force_original_aspect_ratio - If you can want to keep the desired window size, you can add the pad option:
pad=640:480:(ow-iw)/2:(oh-oh)/2, with this option, you can output the video in the desired bound box.
- resize the media or photo resource
- Overlay
ffmpeg -v error -y -i (video) -i (pic) -filter_complex "overlay" output_file.extension- adjust the transparency of the overlay
-filter_complex "[1:v]colorchannelmixer=aa=0.4[transparent_log];[0:v][transparent_log]overlay"aaAdjust contribution of input red, green, blue and alpha channels for output alpha channel. Default is 1 for aa, and 0 for ar, ag and ab.
- multiple overlay, overlay the video with logo at first, then set a label to them. Overlaying the previous output and the third input video
- Drawing text and or timeCode
- fixed text when play
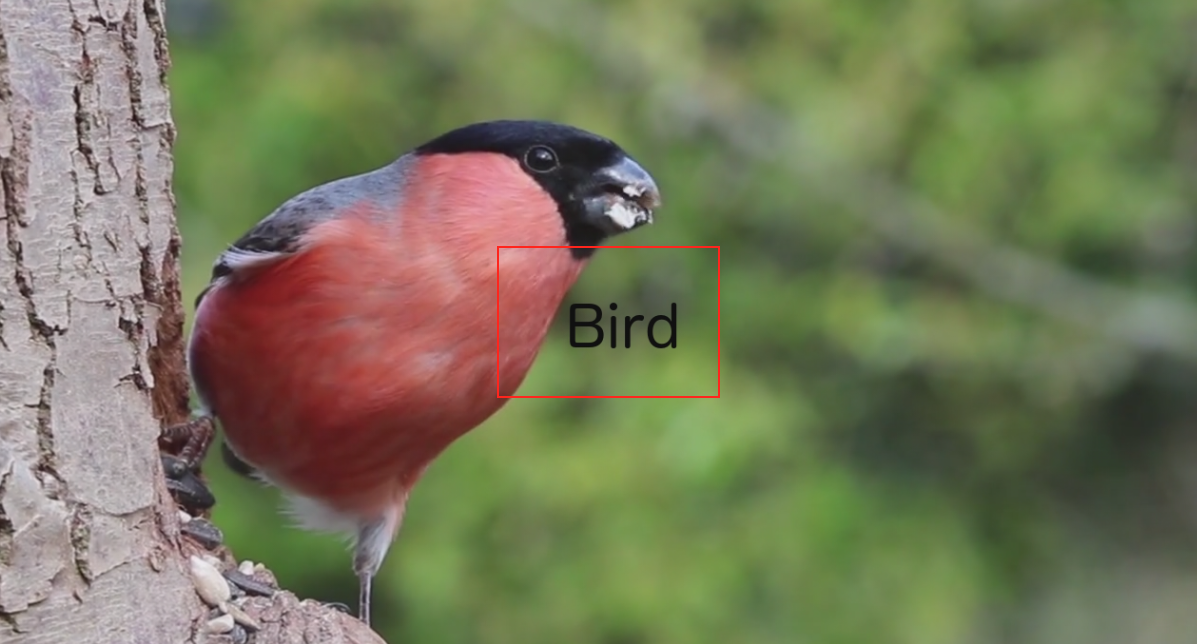
ffplay bullfinch.mov -v error -an -vf "drawtext=text=Bird"- with parameter
xandy, you can adjust its position, likeffplay bullfinch.mov -v error -an -vf "drawtext=fontfile=Example.ttf:text=Bird:x=(w-text_w)/2:y=(h-text_h)/2:fontsize=60"
- moving text when play
- with parameter
twhich represents the time, if you want the text from the top to the center you can use the following command:y=t*50- Generally speaking, If you want to move the text from the right to the left, you can add the parameter
x=(w-text_w)/2-100*t
- with parameter
- add time code
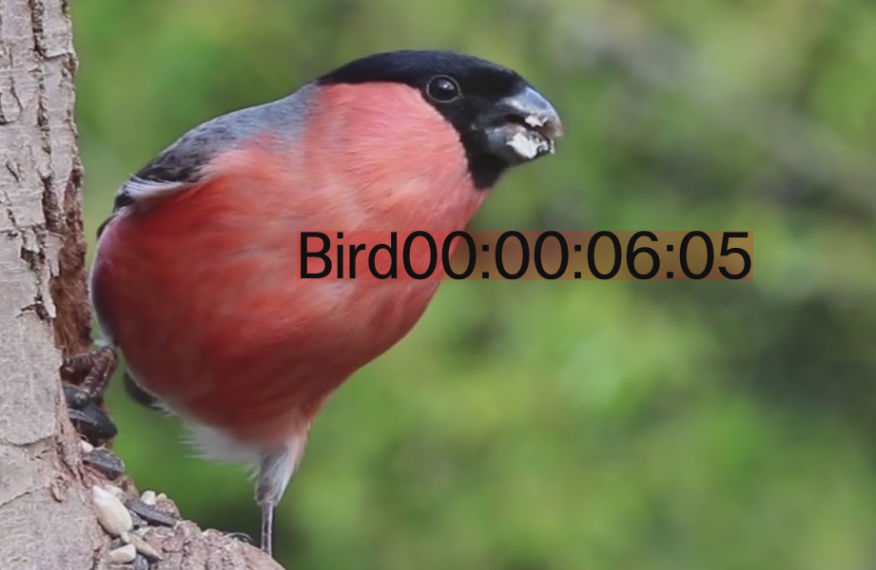
- default
ffplay bullfinch.mov -v error -an -vf "drawtext=fontfile=Example.ttf:text=Bird:x=(w-text_w)/2:y=(h-text_h)/2:fontsize=60:timecode='00\:00\:00\:00':rate='24000/1001'
- with boxColor
:box=1: boxcolor=red@0.2
- default
- fixed text when play
- input & output
- example of manipulation audio
- extract channels
- some channels play the voice, and some channels play the background music
- with filter
amerge=inputs=2, you can merge the whole stream to a one stream with multiple channels - with the following command you can split the whole stream into different files
ffmpeg -v error -y -i two-stereo-tracks.m4a -filter_complex "amerge=inputs=2,asplit=4[all0][all1][all2][all3];[all0]pan=mono|c0=c0[ch0];[all1]pan=mono|c0=c1[ch1];[all2]pan=mono|c0=c2[ch2];[all3]pan=mono|c0=c3[ch3]" -map \[ch0\] ch0.m4a -map \[ch1\] ch1.m4a -map \[ch2\] ch2.m4a -map \[ch3\] ch3.m4a- with the filter
asplitlike[in] asplit=<output number> [out0][out1][out2], you can get number of output - with the filter
pan, you can manipulate the audio
- with the filter
- with filter
- some channels play the voice, and some channels play the background music
- mix channels
- with
ffmpeg -v error -y -i ch0.m4a -i ch1.m4a -i ch2.m4a -i ch3.m4a -filter_complex "amerge=inputs=4" mix_four_in_one_channel.m4a - with the filter
amix=inputs=<number of input>, it can work, but the mixed audio will drop down the volume - with
"amerge=inputs=4,pan=mono|c0=c0+c1+c2+c3", you can avoid this issue
- with
- extract channels
- overview of how to edit media
- Title: ffmpeg basic concept
- Author: Xiao Qiang
- Created at : 2023-03-05 11:56:02
- Updated at : 2025-08-06 15:16:17
- Link: http://fdslk.github.io/tech/video/ffmpeg/2023/03/05/ffmpeg_basic_concept/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
Comments
 * If you don't need any log, you can input the following command, `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format`, you will retrieve the whole video format details
* If you don't need any log, you can input the following command, `ffprobe -v error bunny_1080p_60fps.mp4 -show_format`, you will retrieve the whole video format details